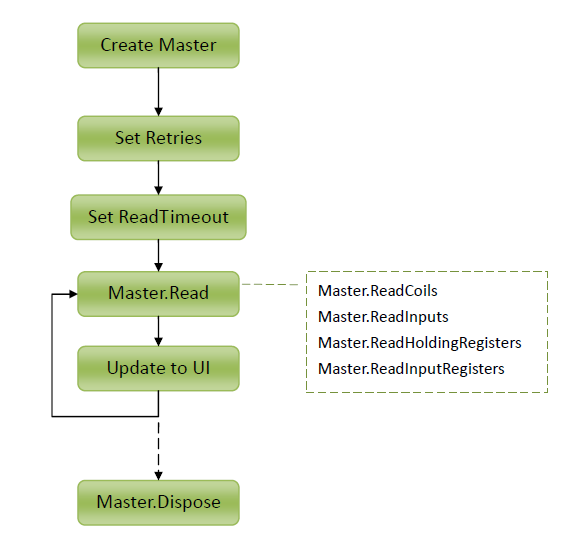
1. CreateRtu
2. Retries[Property]
3. ReadTimeout[Property]
4. ReadCoils
5. ReadInputs
6. ReadHoldingRegisters
7. ReadInputRegisters
8. WriteSingleCoil
9. WriteSingleRegister
1. CreateRtu
RTU master create connection to serial port.
Syntax
ModbusSerialMaster CreateRtu(SerialPort serialPort)
Parameters
serialPort
The serialPort is created by new SerialPort(), and serialport is opened by serialPort.Open().
If serialport doesn’t specified value, it will use default property values to open port. For example,a default port name of COM1, the Parity property defaults to the None,the DataBits property defaults to 8, and the StopBits property defaults to 1.
Return Value
Return ModbusSerialMaster.
Examples [C#]
SerialPort serialPort = new SerialPort(); //Create a new SerialPort object.
serialPort.PortName = “COM1”;
serialPort.BaudRate = 115200;
serialPort.DataBits = 8;
serialPort.Parity = Parity.None;
serialPort.StopBits = StopBits.One;
serialPort.Open();
ModbusSerialMaster master= ModbusSerialMaster.CreateRtu(serialPort);
2. Retries[Property]
[Property]Number of times to retry sending message after encountering a failure
such as an IOException, TimeoutException, or a corrupt message.
Syntax
int Retries { get; set; }
Examples
string ipAddress = “10.0.0.69”; //use TCP for example
int tcpPort = 502;
TcpClient tcpClient = new TcpClient();
tcpClient.BeginConnect(ipAddress, tcpPort, null, null);
ModbusIpMaster master = ModbusIpMaster.CreateIp(tcpClient);
master.Transport.Retries = 0;
Remarks
Default Value is Retries = 3.
It doesn’t need to retry in NModbus and set Retries = 0.
3. ReadTimeout[Property]
[Property]Gets or sets the number of milliseconds before a timeout occurs
when a read operation does not finish.
Syntax
int ReadTimeout{ get; set; }Examples[C#]
SerialPort serialPort = new SerialPort(); //use RTU for example
serialPort.Open();
ModbusSerialMastermaster = ModbusSerialMaster.CreateRtu(serialPort);
master.Transport.ReadTimeout = 300; //millisecondsRemarks
ReadTimeout recommended value
a. RTU:ReadTimeout = 300
b. TCP: ReadTimeout = 1500
4. ReadCoils
Read coils status.
Syntax
bool[] ReadCoils( byte slaveID, ushort startAddress, ushort numOfPoints )Parameters
slaveID Address of device to read values from.
startAddress Address to begin reading.
numOfPoints Number of coils to read.
Return Value
Return bool[].
Examples
byte slaveID = 1;
ushort startAddress = 0;
ushort numOfPoints = 10;
bool[] coilstatus = master.ReadCoils(slaveID , startAddress , numOfPoints);
5. ReadInputs
Read input status.
Syntax
bool[] ReadInputs(byte slaveID, ushort startAddress, ushort numOfPoints)
Parameters
slaveID Address of device to read values from.
startAddress Address to begin reading.
numOfPoints Number of discrete inputsto read.
Return Value
Return bool[].
Examples
byte slaveID = 1;
ushort startAddress = 0;
ushort numOfPoints = 10;
bool[] status = master.ReadInputs(slaveID, startAddress, numOfPoints);
6. ReadHoldingRegisters
Read holding registers value.
Syntax
ushort[] ReadHoldingRegisters(byte slaveID, ushort startAddress, ushort numOfPoints)Parameters
slaveID Address of device to read values from.
startAddress Address to begin reading.
numOfPoints Number of holding registersto read.
Return Value
Return ushort[].
Exampls
byte slaveID = 1;
ushort startAddress = 0;
ushort numOfPoints = 10;
ushort[] holding_register = master.ReadHoldingRegisters(slaveID, startAddress, numOfPoints);
7. ReadInputRegisters
Read input registers value.
Syntax
ushort[] ReadInputRegisters(byte slaveID, ushort startAddress, ushort numOfPoints)Parameters
slaveID Address of deviceto read values from.
startAddress Address to begin reading.
numOfPoints Number of input registersto read.
Return Value
Return ushort[].
Examples
byte slaveID = 1;
ushort startAddress = 0;
ushort numOfPoints = 10;
ushort[] register = master.ReadInputRegisters(slaveID, startAddress, numOfPoints);
8. WriteSingleCoil
Write a coil value.
Syntax
void WriteSingleCoil(byte slaveID, ushort coilAddress, bool value)Parameters
slaveID Address of the device to write to.
coilAddress Address to write value to.
value If the address is going to be written, the value is TRUE.
If the address isn’t going to be written, the value is FALSE.
Return Value
The function doesn’thave return value.
Examples
byte slaveID = 1;
ushort coilAddress = 1;
bool value = true;
master.WriteSingleCoil(slaveID,coilAddress,value);
9. WriteSingleRegister
Write a holding register value.
Syntax
void WriteSingleRegister(byte slaveID, ushort registerAddress, ushort value)
Parameters
slaveID Address of the device to write to.
registerAddress Address to write value to.
value Value to write.
Return Value
The function doesn’thave return value.
Examples
byte slaveID = 1;
ushort registerAddress = 1;
ushortvalue = 1000;
master.WriteSingleRegister(slaveID, registerAddress, value);